The Power of Trees in Our Cities
Hey tree enthusiasts! I’d like to delve into a topic close to my heart: Tree Equity. This concept goes beyond mere greenery; it’s about ensuring every community, especially those historically underserved, benefits from the joys and advantages of trees. I’ve been exploring the Tree Equity Score, a fascinating tool that focuses on this topic.
Why Does Tree Equity Matter?
Tree equity aims to ensure the fair distribution of trees in communities, regardless of wealth. It recognizes the many benefits trees offer, from improving air quality to reducing stress. Wealthier neighborhoods often have more trees, while lower-income areas suffer from the negative effects of inadequate tree cover. Tree equity addresses this by advocating for strategic planting in disadvantaged communities. It also acknowledges the economic and social benefits of well-forested neighborhoods. For more on this, check out American Forests for a deeper understanding of why tree equity is crucial.
A Look Back: How History Shapes Our Urban Forests
Redlining, a policy from the early 20th century, systematically denied financial services to minority neighborhoods, leaving a lasting impact on tree coverage. These marginalized areas face environmental and health disparities compared to wealthier, predominantly white neighborhoods. Understanding redlining’s historical context reveals the unequal distribution of green spaces and urban heat islands. This historical context is crucial to understanding current disparities. From a historical perspective, NCRC’s article on redlining provides valuable insights.
Demystifying the Tree Equity Score
The Tree Equity Score measures tree coverage in neighborhoods, helping identify areas that need more trees. It ensures every neighborhood has enough trees for their benefit. By using advanced technology, American Forests has created a database that assesses tree coverage block-by-block. The map shows areas lacking trees and helps prioritize planting efforts. The website offers an easy-to-use interface to explore data and take action. Cities across the US are using this tool to guide reforestation programs. The Tree Equity Score promotes equal access to tree benefits and creates greener and fairer cities.
The Real Impact of Tree Equity
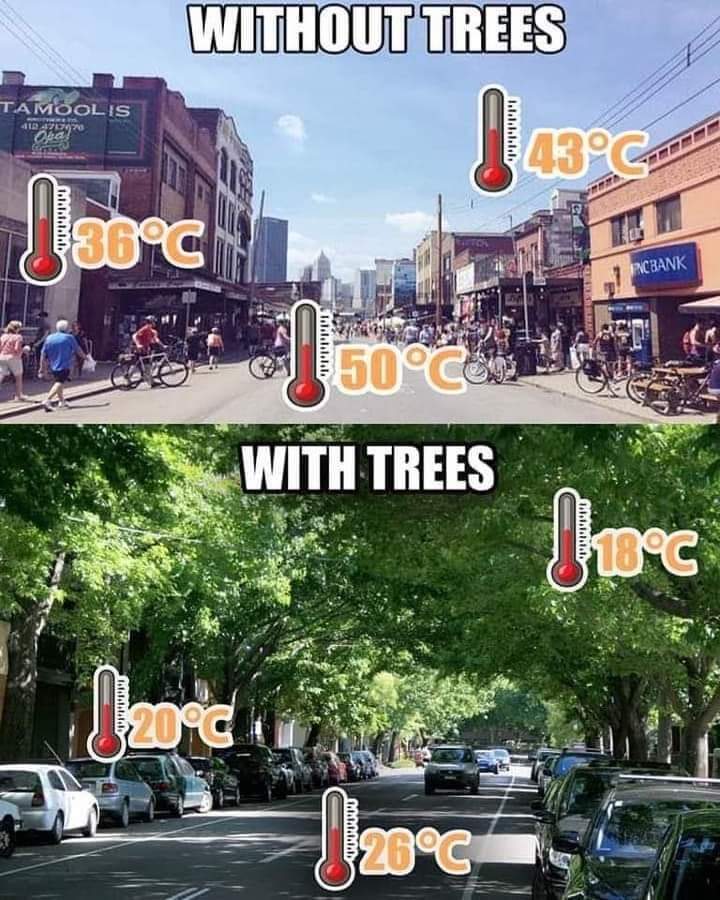
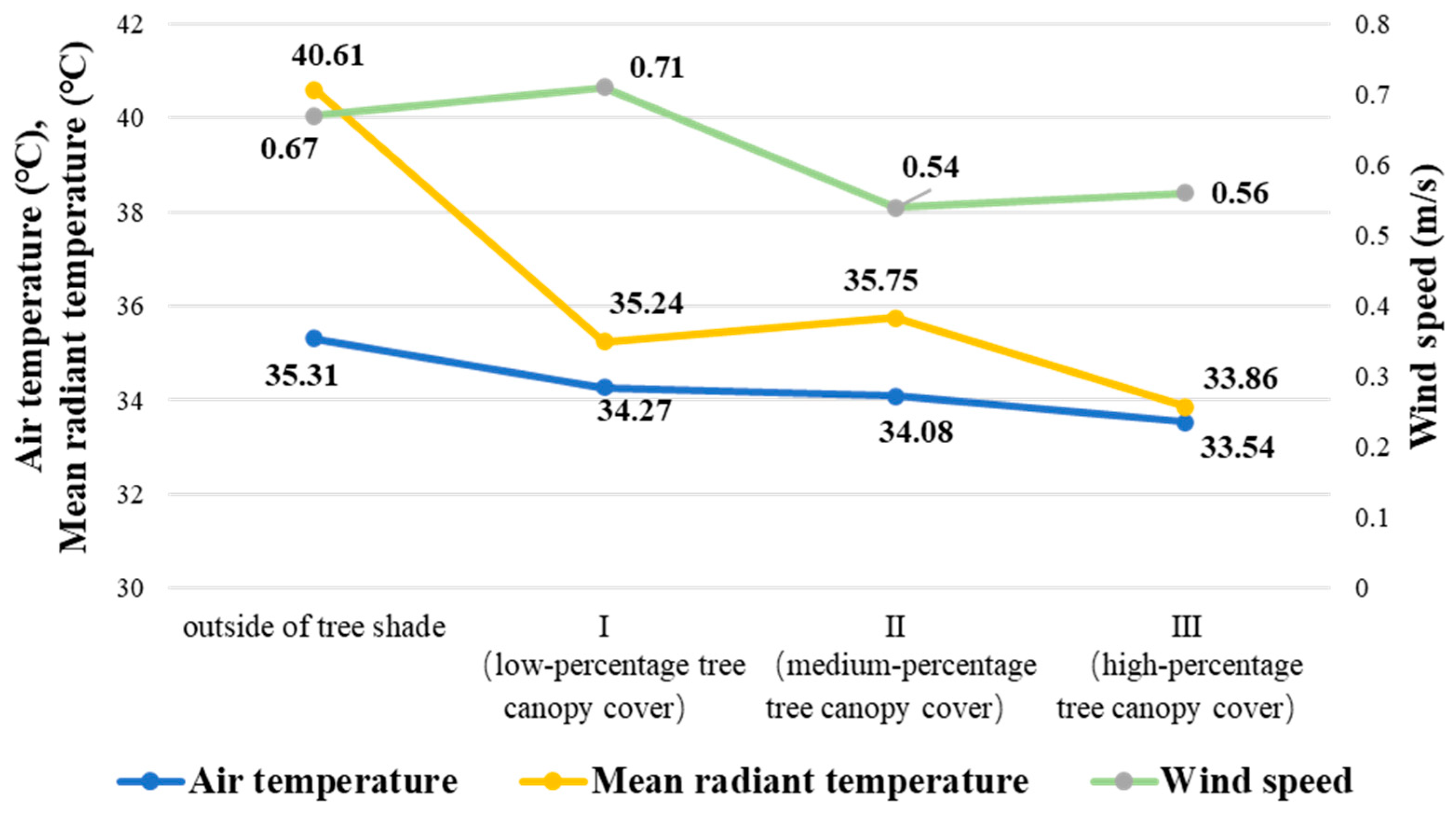
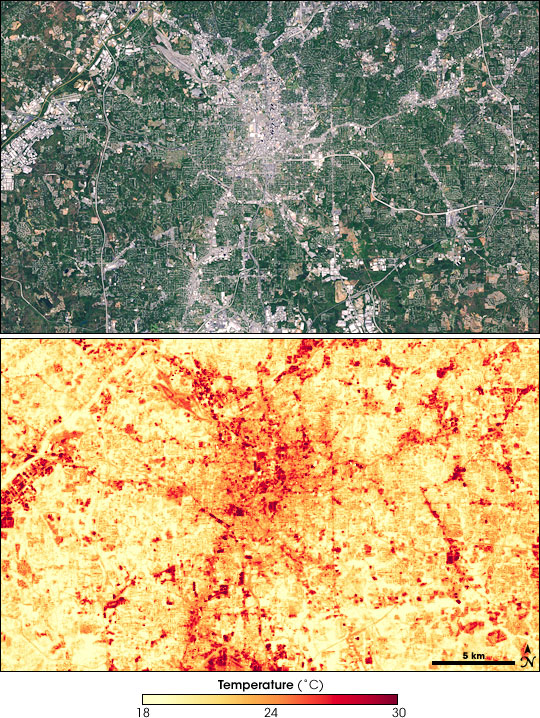
Tree equity goes beyond aesthetics and includes air quality and temperature regulation. Trees act as natural filters, absorbing pollutants and releasing oxygen, improving air quality. They also regulate temperature, reducing the heat island effect in urban areas. Efforts are being made to enhance tree coverage through tree-planting campaigns and community programs. The USDA Forest Service’s Urban Forests page provides valuable information on the benefits of urban forests and the importance of tree equity in promoting sustainability. Increasing tree coverage can create healthier, more sustainable environments for future generations.
New Policies: A Ray of Hope
New policies to reduce inflation and promote environmental justice bring hope. They focus on bringing more trees to communities that need them the most, improving their quality of life. The Inflation Reduction Act aims to address economic disparities and enable low-income households to access essential resources like trees. The Justice40 campaign seeks to rectify historical injustices by directing 40% of climate and clean energy benefits to disadvantaged neighborhoods. The EPA’s Justice40 Initiative provides valuable information on these policies, emphasizing community engagement and collaboration.
Final Thoughts
Tree equity is essential for a greener and fairer future. It ensures that all communities, regardless of their socio-economic status, have equal access to the benefits of trees. By planting trees in underserved neighborhoods, we improve residents’ quality of life and create spaces for them to connect with nature. Moreover, trees can improve air quality and public health by absorbing pollutants and reducing stress levels. Prioritizing tree equity is not only about the environment but also about social justice, as marginalized communities have historically faced environmental injustices. We should be working together to create a world where every community thrives under the shade of trees.









:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/56814733/shutterstock_262710809.13.jpg)